Configuring SSH for Git Server:
In order to set up a Git server to work over SSH, you have to make sure SSH is installed and is running correctly.
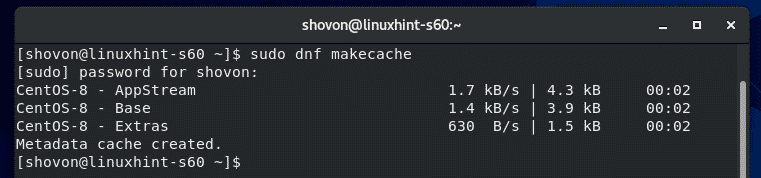
First, update the CentOS 8 package repository cache with the following command:
Now, install SSH server with the following command:
It should be installed. In my case, it was already installed.
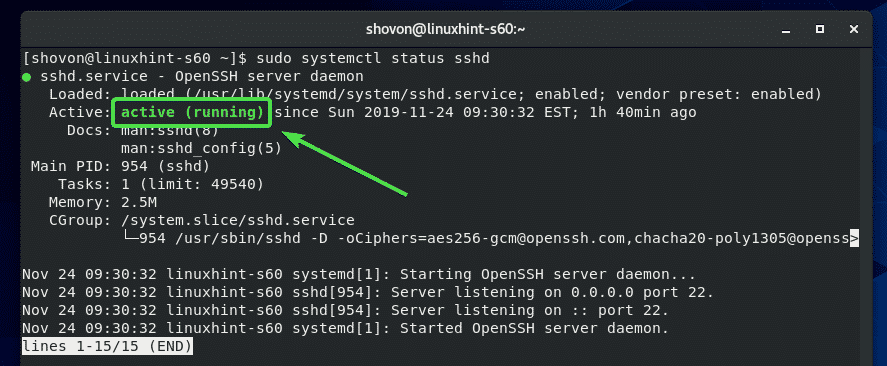
Now, check whether the SSH service is running with the following command:
The SSH service should be running as shown in the screenshot below.
If for some reason, the SSH service is not running for you, you can start it with the following command:
Now, allow access to the SSH ports through the firewall with the following command:
Finally, run the following command for the firewall configuration changes to take effect:
Installing Git:
Now, you can install Git with the following command:
To confirm the installation, press Y and then press <Enter>.
Git should be installed.
Creating a Dedicated User for Hosting Git Repositories:
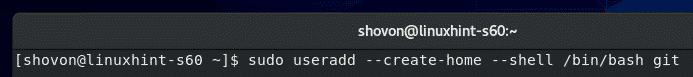
Now, create a dedicated user git with the following command:
Now, login as the git user with the following command:
Now, create a new directory ~/.ssh as follows:
Only the git user should have read, write and execute permission to the ~/.ssh directory.
To do that, run the following command:
As you can see, now only the user git has read, write and execute permission to the directory.
Now, create a new file ~/.ssh/authorized_keys as follows:
Only the git user should have read and write permission to the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file.
To do that, run the following command:
As you can see, now only the user git has read, and write permission to the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file.
Adding Client public Key to the Git Server:
To access the git repositories on the Git server, the users of the repository must add their public keys to the Git server.
The users can generate their SSH keys with the following command:
Press <Enter>.
Press <Enter>.
Press <Enter>.
The SSH key should be generated.
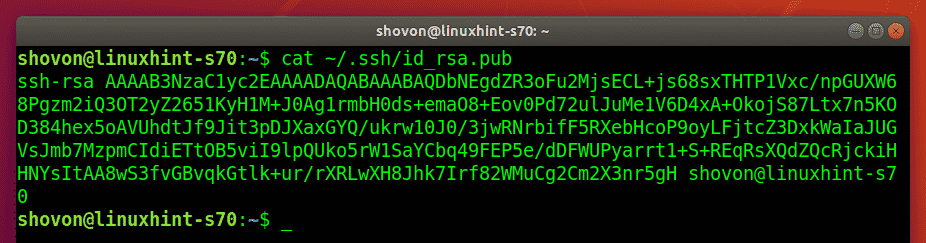
Now, the users can find their public key in the ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub file.
Now, the users should send their public keys to the Git server administrator and the server administrator can add these keys to the Git server.
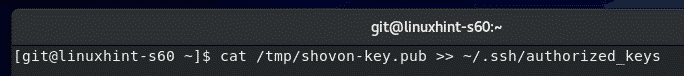
Let’s say, the server administrator has uploaded the public key file to the Git server. The file is in the path /tmp/shovon-key.pub.
Now, the server administrator can add the contents of the public key to the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file as follows:
The public key should be appended to the end of the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file.
Creating an Empty Git Repository on the Git Server:
In the home directory of the git user, we will keep all our Git repositories that authorized people can access.
To create an empty Git repository test on the Git server, run the following command:
If an authorized user wants to access the Git repository from the Git server, all he needs is the name of the Git repository and the IP address of the Git server.
To find the IP address of the Git server, run the following command:
The IP address in my case is 192.168.20.129. It will be different for you. So, make sure to replace it from now on.
A new directory test.git should be created on the Git server.
Accessing Git Repositories from Git Server:
Now, an authorized user can access the test Git repository we’ve created earlier as follows:
If the user is connecting to the Git server for the first time, he/she will have to type in yes and press <Enter>.
The Git repository test should be cloned.
A new directory test/ should be created in the users current working directory.
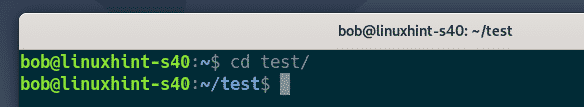
The user will have to navigate to the test/ directory as follows:
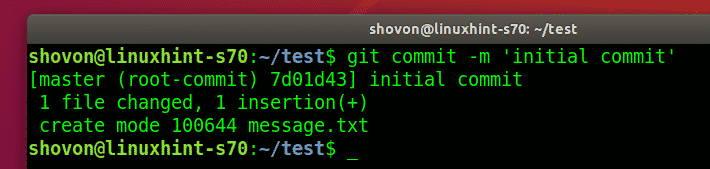
Let’s say, the user created a new file.
Committed the changes.
$ git commit -m ‘initial commit’
Then, the user pushed the changes to the Git server.
Adding Another Team Member:
If another user wants to access the Git repository test, he will have to generate an SSH key and send the public key to the Git server administrator. Once the Git server administrator adds his/her public key to the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file, the user can access the Git repositories on the server as well.
Let’s say, bob also wants to work on the test Git repository.
He clones the test Git repository on his computer.
bob types in yes and presses <Enter>.
The test Git repository is cloned.
bob navigates to the test/ directory.
Finds the commit that the person working on this Git repository made.
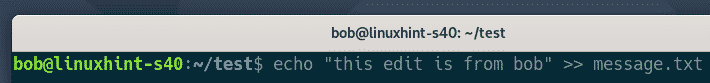
He makes some changes to the project.
Commits the changes.
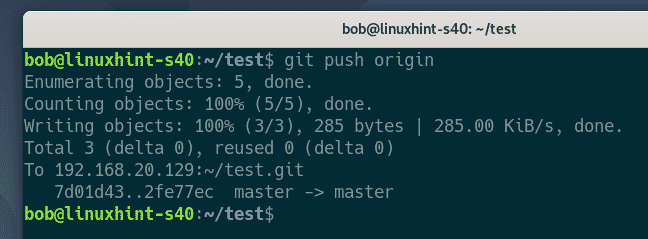
bob pushes the changes to the Git server.
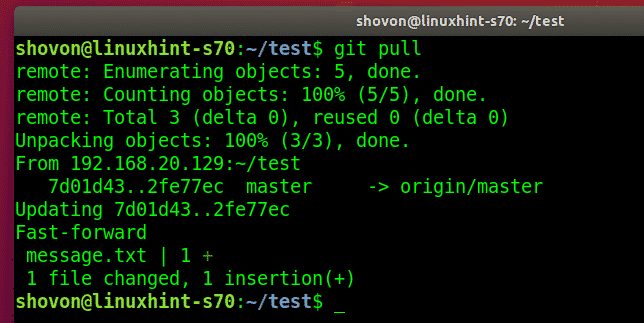
Now, the other user shovon pulls the changes (if any) to Git repository from the Git server.
shovon finds the new commit that bob made.
So, that’s how you configure a Git server with SSH on CentOS 8 and use it. Thanks for reading this article.