Method of Installing the NIS Server on Debian 10:
For installing the NIS server on a Debian 10 machine, you will have to perform three basic steps:
Step # 1: Update your Debian 10 System:
First, you have to update your system with the following command:
After successfully updating your system, you will receive the messages shown in the image below:
Step # 2: Install the NIS Server on your Debian 10 System:
Now, we can install the NIS server with the following command:
Step # 3: Set up the Domain Name for your NIS Server on Debian 10:
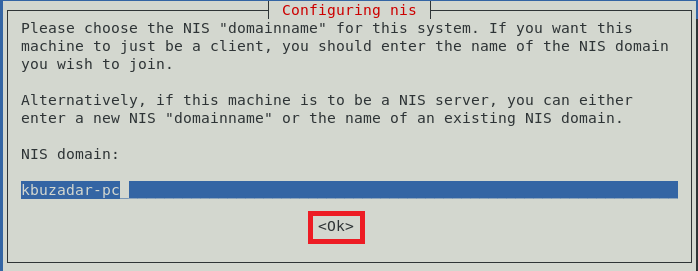
During the NIS server’s installation, you will be asked to set up the domain name for it. You can have any name of your choice, or you can either go with the default one and press the Enter key as we did.
After setting up the domain name for your NIS server, you will notice that the installation will finish within a few seconds while displaying the messages shown in the image below on the terminal:
Method of Configuring the NIS Server on Debian 10:
After installing the NIS server on Debian 10, we can now go on with its configuration steps as follows:
Step # 1: Start the “rpcbind” Service on Debian 10:
First, we need to start the “rpcbind” service on Debian 10 with the command shown below:
Step # 2: Check the Status of the “rpcbind” Service on Debian 10:
Now, we will check whether the “rpcbind” service has been successfully started or not by running the following command:
You can easily see the status of the “rpcbind” service on our Debian 10 system highlighted in the image below:
Step # 3: Start the “ypserv” Service on Debian 10:
After that, we will start the “ypserv” service on Debian 10 with the following command:
Step # 4: Check the Status of the “ypserv” Service on Debian 10:
Now, we will check whether the “ypserv” service has been successfully started or not by running the command shown below:
You can easily see the status of the “ypserv” service on our Debian 10 system highlighted in the following image:
Step # 5: Set NIS as the Master Server on Debian 10:
Now we will set the NIS as the master server on Debian 10. For that, we will access the /etc/default/nis file with the command shown below:
This file is shown in the following image:
We will then assign the value “master” to the “NISSERVER” variable, as highlighted in the image shown below. After that, we can save and close our file.
Step # 6: Set up the Allowable Access IP Range on Debian 10:
Now, we will set up the IP range to allow access to our NIS server. For that, we will access the /etc/ypserv.securenets file with the following command:
This file is shown in the image below:
Now, we will comment out the line shown in the following image:
Finally, we will add the allowable IP range to the end of this file, as shown in the image below. After that, we can save and close our file.
Step # 7: Add an IP Address for your NIS Server on Debian 10:
Now, we can add any desired IP address for our NIS server. For that, we have to access the /etc/hosts file with the command shown below:
We need to locate our NIS server’s name in this file and then assign any desired IP address or even go with the default one as highlighted in the following image. After that, we can save and close this file.
Step # 8: Restart the NIS Server on Debian 10:
After making all these configurations, we will restart the NIS server with the following command:
Step # 9: Update the NIS Database on Debian 10:
Finally, we will update the NIS database with the command shown below:
At this point, we can add any hosts to this database that will be running the NIS servers. Once you have added the hostnames, you can press Ctrl+D.
After that, you have to enter “y” and then press the Enter key as highlighted in the following image:
Once the NIS database is updated, you will get a confirmation message that the selected system has been set up as a NIS master server, as highlighted in the image shown below:
Method of Removing the NIS Server from Debian 10:
We can also remove the NIS server from our Debian 10 system any time by going through the following two steps:
Step # 1: Remove the NIS Server along with its Configuration Files:
First, we will run the command shown below to remove the NIS server and its configuration files:
Step# 2: Remove all the Additional Packages and Dependencies:
Finally, we will also remove all the unused packages and dependencies with the following command:
Conclusion:
This article focused on the methods of installing and configuring the NIS server on Debian 10. The methods might look lengthy, but it only took us a few minutes to complete these configurations. Finally, we wrapped up this article with the removal method of NIS from Debian 10.