Syntax
Let’s examine the above syntax for this query:
- Table_name: is the title of an existing table you want to modify.
- existing_column_name: is the name of a column to be deleted.
Note: You can have more than one columns to be deleted. For that, you have to use more than one DROP COlUMN clause in your query.
Drop Column via MySQL Workbench
Make sure you have MySQL installed on your windows system. You have to open the newly installed MySQL workbench from the start button of your desktop. We have to make sure to connect our MySQL workbench with the database from the main menu of the workbench under the ‘Database’ tab.
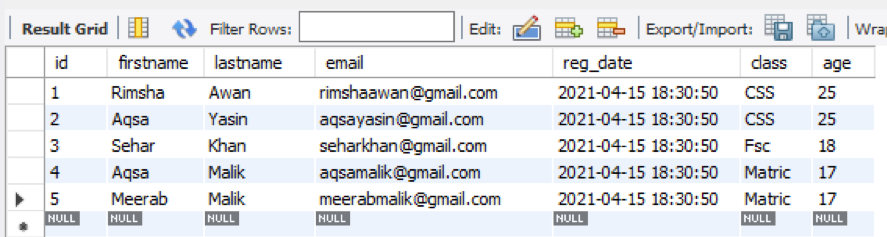
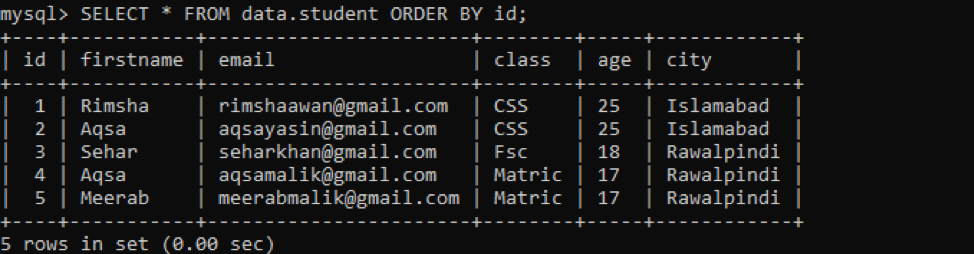
Under the workbench’s Navigation bar, we have a list of different databases that we have created already. Within the database ‘data’, we have added a table ‘student’. The table ‘student’ has the following records in it as below.
If you want to drop a column from an existing table ‘student’, you have to sail across in the direction of the Schemas beneath the Navigator. Inside the database ‘data’, we have a list of tables, e.g., student and teacher. We will expand the table ‘student’. While hovering over it, you will discover a representation of the setting icon, as shown below. Hit it off to carry on.
A new window will be opened in the workbench as below. We might see a list of columns and their definitions. To drop a column from the table, you have to select that column, right-click on it and press the ‘Delete Selected’ option.
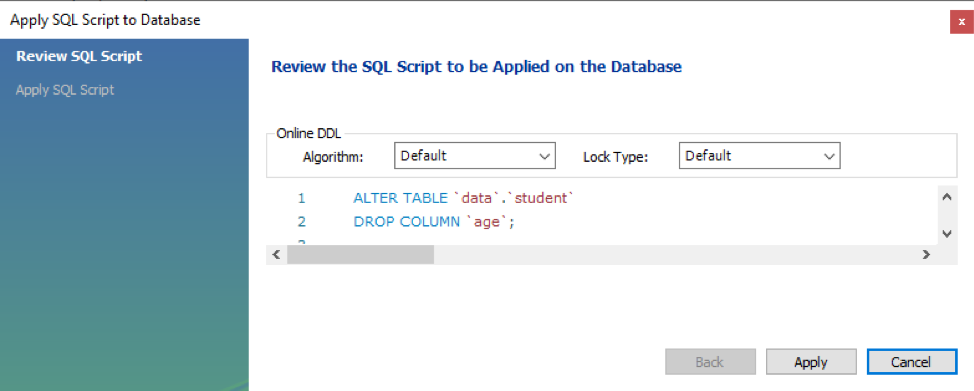
A new window will be popped up, having a query written on it to drop a column. Hit on Apply button to proceed with the update.
Another below window will be opened. Tap on a Finish button to reflect changes at the table ‘student’.
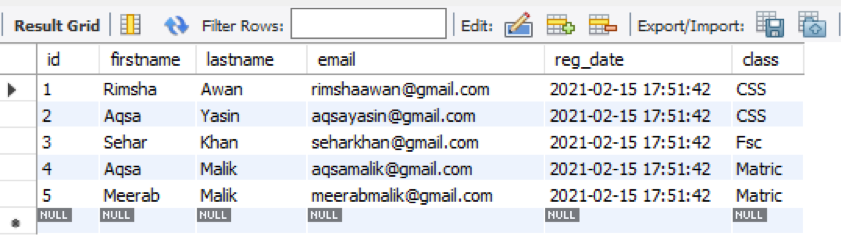
You can see a column ‘age’ has been removed from the table ‘student’ as we couldn’t find it here.
Try the below query in a workbench query place below the navigator to drop a column from a table. Tap on the flash icon under the navigator bar as highlighted in the image below to reflect the query’s changes.
The new altered table without a column ‘age’ is shown below.
Drop a Column via Command-Line Shell
Make sure you have a command-line client shell utility of MySQL has been installed on your current system. To remove a column from a table while using the command-line, open the MySQL command-line client from the taskbar. Type your MySQL password while asked in the shell to continue working.
Suppose we have a table ‘student’ with some record in it residing in the schema ‘data’. While checking, we have found a given-below record in the table ‘student’. Right now, this table has probably 9 columns in it.
Example 01: Drop a Single Column
If you are looking for an example to delete a single column from an existing table, then this example is indeed for you. Considering the same above table, let’s delete the column named ‘lastname’ from it. After that, we must have 8 columns left. Try the below query in the MySQL command-line client shell. If the query works properly, it will display a message that the query is ‘OK’.
The above image shows that the query works properly, and the column ‘lastname’ has been removed from the table ‘student’. Let us check it and use the same SELECT query to call the table ‘student’.
The output below shows that we have left with only 8 columns, and the column ‘lastname’ and its values have been deleted from the table ‘student’ successfully.
You can delete columns from the start, last, middle, and from any position of the table.
Example 02: Drop More than One Columns
You’re also able to drop more than one column from any table in MySQL using the ALTER query. You just need to add more than one DROP clause in the ALTER query. Let’s take the same above updated table ‘student’ having 8 columns. We have to delete the two columns, e.g., gender and reg_date, from it. For that, we have to use two DROP Column clauses in our query. Let us execute the below ALTER query followed by the DROP clauses in the MySQL command-line client shell.
As you can see from the above query message that the query worked perfectly. Upon checking the table ‘student’, we have got an updated table having 5 columns left in it. The column named ‘gender’ and ‘reg_date’ has been removed from it.
Point to be noted that we have deleted the columns reg_date and gender from two different locations of a table. This means you can delete any column from any location of a table. It is not necessary to delete columns from the last place of the table.
Conclusion
You have proficiently tried all the inquiries to delete, remove or drop a single column or more than one column from an already defined table in a database while working in MySQL workbench and Command-line client shell. We hope you have got no issues while trying all the above methods.